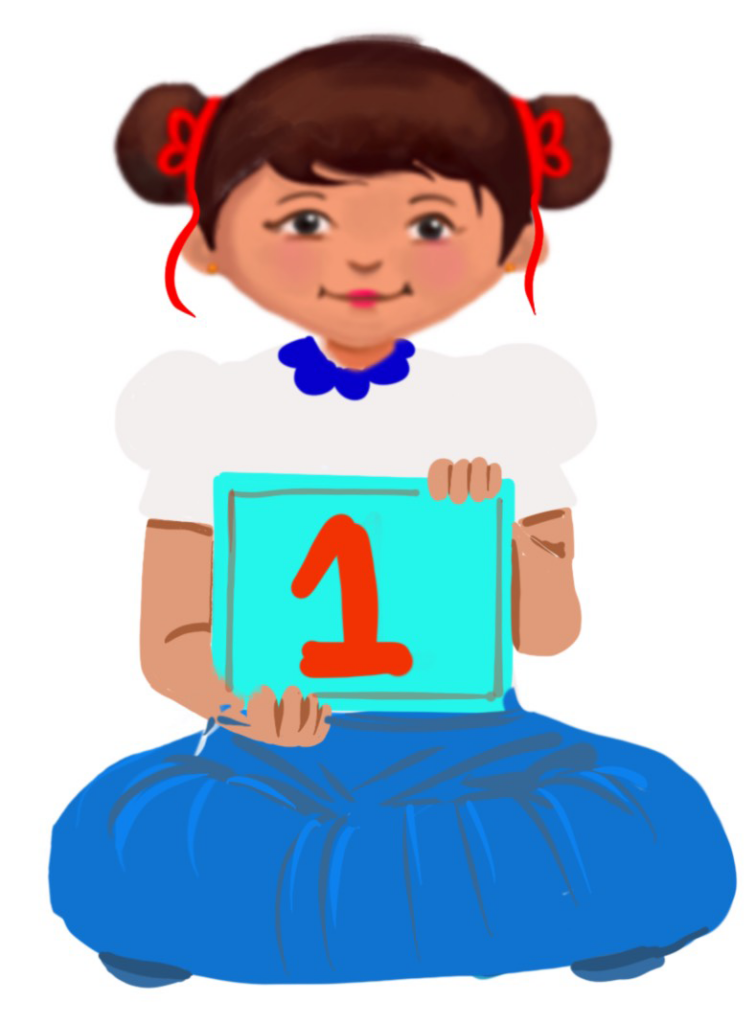

Parts of a Computer
Class 1
 Objective
Objective
Students will be able to name the parts of the computer and describe their functions.
 Pre-requisites
Pre-requisites
| Students should know i) What a computer is ii) Where and why a computer is used. |
 Goal
Goal
All
All children will be able to recognise the parts of the computer.
Some
Some children will be able to name the parts of the computer.
Few
Few children will be able to describe the functions of the parts of the computer.
Operational Definition
All – This gives the goal, which is the minimum that the teacher must achieve for all students in the classroom.
Some – This gives the goal that the teacher may try to achieve for some students in the classroom who can achieve the suggested goal over and above the goal stated for ‘All’.
Few – This gives the goal that the teacher may try to achieve for few students in the classroom who can achieve the suggested goal over and above the goal stated for ‘Some and ‘All’.
Materials required:
Technology
- An Internet and audio-enabled computer, smartboard projector, and screen.
- All devices like laptops, tablets and desktop computers with accessibility features enabled.
- Screen readers like JAWS and NVDA.
- Large keyboards, built-in screen magnifiers, hearing aids, text-to-speech and speech-to-text software.
- Voice recognition software like Siri, Windows Speech Recognition, headsets, etc.
- Student writing or typing tools.
Teacher Materials
- Whiteboard and markers or blackboard and chalk.
- Pre-teach vocabulary cards, sight words, communication cards and worksheets.
- Lesson videos.
Student Handouts
- Handout 1: Communication Cards
- Handout 2: Vocabulary Cards
- Handout 4: Trace and Learn Card
- Handout 5: Yes or No Cards
- Handout 6: Thumbs Up and Down Card
- Handout 7: Worksheets
Print Preparation
The teacher will print, copy or laminate (wherever applicable):
- Communication Cards for students
- Trace and Learn Cards for students
- Vocabulary Cards for students
- Thumbs up and Thumbs down Card for students
- Yes or No Cards for students
- Pre-teach vocabulary cards, sight words cards, sight words
- Worksheets for students
Preparation of Activity:
- All the learning and teaching materials needed for this lesson plan must be ready before the lesson begins.
- Ensure that there are enough copies for all children. Multiple copies can be made by photocopying too.
- Please have the assistive technologies and accessibility features ready for your inclusive classroom.
Setting for the lesson transacting:
This topic must be taught in the classroom or a computer lab.
Instructions to the teacher:
- Begin the topic with a Pre-assessment worksheet and Pre-teach vocabulary
1. Expected Prior Knowledge
Awareness of the extent of student’s prior knowledge of the topic will help the teacher plan and deliver the lesson appropriately. This could be assessed through the provided worksheet.
Worksheets, Vocabulary words
Worksheet: Pre-assessment
Worksheet: Colour the Sight words
LTM: Vocabulary Sight words
LTM: Vocabulary Sight words with pictures
2. Warm-up
1. Write the sentence ‘Parts of the computer’ on the board.
2. Ask students to write down the first word that comes to mind when thinking of the parts of the computer.
Possible Answers: monitor, keyboard, mouse, headphones, CPU, speakers
2. Which part of the computer is used for listening to music?
Possible Answers: headphones, earpods, speakers
3. What do you do with a keyboard?
Possible Answers: type, write, play
DIFFERENTIATION
- Students can write down answers in their notebooks or on a slip of paper and stick it on the corkboard.
- Students can choose to write their answers or communicate their responses verbally with a friend/teacher.
- Students can draw the word or point to the picture on the Communication Card (a Communication Card handout should be provided).
- The teacher should immediately praise the student with his/her name and reward the child.
Worksheets and Communication Cards:
Worksheet: Vocabulary
Worksheet: Trace and Learn
LTM: Thumbs Up and Down
LTM: Communication card
LTM: Yes or No Cards
3. My Friend – The Computer
Oh, my dear friend, the computer,
You are a smart machine,
You have the CPU, monitor and keyboard.
The mouse is my favourite.
You make my work much easier and faster.
Drawing and gaming are fun,
So here is a hug to my computer,
Truly, you are a wonder machine.
Video: My Friend – The Computer
Video: My Friend – The Computer ISL
 Notes to the Teacher:
Notes to the Teacher:
The teacher could play the video and make all the students listen to the music and do the appropriate actions, as shown in the video.
Adaptations to address variability in an inclusive classroom:
The Variability of an Inclusive Environment needs to address the processing and attention differences of the learners. An inclusive environment may have learners with Visual Impairment, Hearing Impairment, Loco-Motor Impairment and Cognitive Differences. Learners not only learn in different ways but also have unique motivations, interests, personalities, and strengths. To address this variability, providing the appropriate adaptation is an effective solution.
Adaptation: Learning to Dance
Adaptation: Adaptation for Dance video
4. Parts of the Computer
Asset objective: Students will learn the computer parts and their functions.
The main parts of the computer are the Monitor, CPU, Keyboard, and mouse. We also connect a Printer and a Speaker to a computer. All these parts are put together to make our computer system.
Poster
LTM: Graphic Organiser 1
LTM: Graphic Organiser 2
Guided Watching
Bring attention to the screen, “Let’s watch this video.
Ask students to give a thumbs up whenever they hear where a monitor, keyboard, mouse, CPU, speaker, headphone, webcam, or microphone is used in the video.
Play videos
Video: Computer and its Parts Real-time
Video: Parts of the Computer Animated (Less information)
Video: Parts of the Computer Animated (Less information)ISL
Video: Parts of the Computer Animated (More information)
Video: Parts of the Computer Animated (More information) ISL
When there are children with hearing impairment in the inclusive class, use the video with Indian Sign Language (ISL)
CPU
CPU stands for Central Processing Unit. It is the most important part of the computer.
Monitor
The computer monitor looks exactly like our television.
It shows us text, photos and movies.
It is also called a screen.
Keyboard
The keyboard has many keys with numbers and letters.
It is used to write on the computer.
Mouse
The mouse is a pointing device. It is used to point at items shown on the monitor.
Other devices connected to a computer
Printer: A printer is used to print on paper.
Speaker: Speakers are used to listening to music.
Microphone: Microphones are used to record sounds.
Headphones: Headphones are used to listen to music without disturbing others.
INFORMAL ASSESSMENT (AFTER PLAYING VIDEOS)
1. Ask, “What are the parts of the computer?”
Structure prompting to get students to come up with a definition using language from the video.
Example: Monitor, keyboard, mouse, CPU, headphone, webcam, etc.
Write the question and definition on the board after student responses.
2. Ask, “Have you seen the parts of the computer?” (The answer is yes)
3. Ask, “Is the keyboard used for typing and piano the same?” (The answer is no)
DIFFERENTIATION
Verbal response
Verbal response or hold up Yes or No card
Hold up or points to Yes or No card
Worksheet: Informal Assessment
 Notes to the teacher:
Notes to the teacher:
- The teacher has to play the video as per the children’s needs.
- Play the revised version of the video first and teach the fundamentals of the computer well.
- Once the children are clear and if the child’s learning potential is good, then the next video could be played.
Suggested Variation in Rules and Pace:
When working with special children, adapting the rules and pace to their specific needs is important. Here are some suggestions:
- Vary the rules: You can adapt the rules for this topic depending on the child’s abilities. This lesson plan contains different ways of student-teacher interaction worksheets like the Wh cards, Trace and Learn cards, Vocab cards, Yes or No cards, etc. Choose the appropriate worksheet based on the needs of the children. Different ways of teaching the parts of computer are provided throughout the lesson plan, the teacher can choose the appropriate ones.
- Vary the pace: Some children may need more time to complete the tasks than others. It may be helpful to break up the task into smaller parts, providing regular breaks or alternate activities to avoid frustration or fatigue. You can also use a timer to help the children pace themselves and feel accomplished as they work towards completing the task.
- Provide additional support: You can provide adaptive tools such as pencil grips for children with fine motor difficulties.
- Positive feedback: Providing positive feedback throughout to build the child’s confidence and motivation is essential. Be specific and provide feedback for effort, progress, and quality of work.
Adaptations to address variability in an inclusive classroom
The Variability of an Inclusive Environment needs to address the processing and attention differences of the learners. An inclusive environment may have learners with Visual Impairment, Hearing Impairment, Loco-Motor Impairment and Cognitive Differences. Learners not only learn in different ways but also have unique motivations, interests, personalities, and strengths. To address this variability, providing the appropriate adaptation is an effective solution.
Adaptations to address learner variability: Parts of the Computer
5. I Spy Computer Parts
Asset Objective: Learners will be able to identify the parts of the computer.
Aim: To recognise the parts of the computer through fun and also develop oral skills.
Resources required: Printouts of ‘I Spy Computer parts’ worksheet
Setting for the activity: Group activity/Indoor
Type of Activity: Games
Preparation of Activity: Printouts necessary for the game must be taken before the activity. The class has to be divided into six groups. Each student should be provided with the printouts. Each group has to have a peer buddy.
Role of the Teacher: Observer
Role of a peer buddy: The peer buddy should encourage the learners with disabilities to come up with answers and share their responses with the class or among the group. Peer buddies could also record the responses or help them write and fill in the worksheet.
Procedure:
i) One player among the group chooses an object that they can see and says, “I spy with my little eye something beginning with …” naming the first letter of the object’s name.
ii) Other players must guess the chosen object until someone guesses correctly.
Observation:
‘I Spy’ is a turn-taking game. It helps to develop a child’s social skills. Students are seen learning how to cooperate with others. This game is great for learning vocabulary, which helps them remember the parts of the computer.
Conclusion: This game will help the students recognise computer parts.
Suggested Variation in Rules:
The children could count the number of each computer part. Note down in the appropriate boxes individually without playing it as a game.
Worksheet: I Spy Computer parts
 Notes to the teacher:
Notes to the teacher:
Adapting the ‘I Spy game’ for children of different ages or with diverse abilities.
If children cannot recall the parts of the computer, they could also say, ‘I spy with my little eyes something in red’ or ‘I spy with my little eyes something that looks like a mouse’. I spy with my little eyes that make a click click sound’.
6. Colour the Computer Parts
Asset Objective: Learners will be able to recognise the parts of the computers and colour them.
Worksheet: Colouring Computer Parts
Worksheet: Parts of Computer Colouring Activity
Adaptation: Colour the Computer Parts
Adaptation Video: Colour the Computer Parts
7. Who am I?
Asset Objective: Learners will be able to elucidate the parts of computers by communicating among themselves till they arrive at the right answers.
Who am I? is a gamified activity in which children have to guess the parts of the computer on the card placed behind their back or on their foreheads.
This game can be played indoors or outdoors.
“Who am I ?” game rules
Take the printouts of the printables provided and make them into cards.
Use a piece of tape or glue them to the back of each child so they cannot see what is written/drawn on it. Cards could also be put on their foreheads using bands.
- Children will have to walk around the room and ask their classmates questions to collect clues to help them guess the right answer.
- Children have to ask questions based on the functions of the parts of the computer and not direct questions.
- If the child asks direct questions, for example: Am I a Monitor, the child loses one point.
- Children must ask questions, but yes or no answers can only be formulated. When the child has guessed the correct word written on his back, he scores 1 point.
Video and Printables:
Video: Who am I?
LTM: Who am I Printables
 Notes to the Teacher:
Notes to the Teacher:
Discipline has to be maintained in the classroom all throughout the game.
8. Craft a Laptop
Aim: To craft a laptop using available materials.
Materials required: Two pieces of cardboard, an A4 sheet of paper, glue, a sketch pen etc
Procedure: A detailed explanation of crafting the laptop is shown in the video.
Video: How to Craft a Laptop
9. Craft Computer and its parts
Aim: To craft a computer and its parts using available materials.
Materials required: cardboard, A4 sheet of paper, glue, sketch pen, etc.
Procedure: A detailed explanation of crafting the laptop is shown in the video
Video: How to Craft a Computer
10. Assessment
Prerequisite:
- Children know the meaning of Computer, Mouse, Keyboard, CPU, and Monitor.
- Children should be able to read the words.
Suggested Variation in Pace:
Students could take a few extra minutes to complete the worksheets.
Suggested Variation in Perceived Challenge:
- Children could also record their responses or answers or use response cards to convey the answers to their peers
- They may also be allowed to dictate their responses (especially students with visual disabilities)
- Students may also be given additional time to complete the worksheet.
- Students could take the assessments using the word wall.
Suggested Scaffolds for Assistance and Practice:
- The teacher could help the students while reading the words.
- Teachers could activate the students’ prior background knowledge by showing the video again.
- Teacher could break the task into smaller, more manageable parts. Students could also express themselves using gestures or visual aids.
- Children who can draw a computer can be allowed to draw, and the rest must colour the picture.
- Video with audio is provided so that students can replay them when needed.
- Students can express their answers orally to their peer buddy if they face writing difficulties.
- Screen enlarger and Screen reader for visually impaired
- Slant boards for students with motor challenges
- Pencil grips also have to be provided for those who need them.
- The Avaz app or any other AAC app or AAC device could also be provided, or children who have communication difficulties can respond by gestures, eye pointing or response cards.
- Audio recorder
Assessment and Wordwall activities
Worksheet: Match Computer Parts
Word Wall: Match Computer Parts
Worksheet: Parts of Computer – Yes or No
Worksheet: Parts of Computer – Yes or No Large font
Word Wall: Parts of Computer – Yes or No
Worksheet: Label the Parts of the Computer
Word Wall: Label the Parts of the Computer
Worksheet: Match the Parts of the Computer to its Functions
Worksheet: Match the Parts of the Computer to its Functions in Large Font
Word Wall: Match the Parts of the Computer to its Functions
Worksheet: Who Am I
Worksheet: Who Am I in Large Font
Word Wall: Who am I
Worksheet: Parts of Computer Wordsearch
Word Wall: Parts of Computer
8. Assistive Technologies
Video: Assistive Technologies
Teacher Resource Document
| Source and Attribution of images: All images used in the above Assets and Aids are originally created. https://pixabay.com/illustrations/computer-keyboard-cpu-monitor-5675047/By Felixmh |
| This digital material has been developed by the Sri Sathya Sai Vidya Vahini Inclusive Education Project, a unit of Sri Sathya Sai Central Trust, Prasanthi Nilayam, as a collaborative offering in the service of our nation. |