
Numbers Stories
Part 2 – Subtraction
Learning Outcome
Comprehends and solves simple two-digit number word problems in subtraction.
 Objective
Objective
Children will solve word problems involving the subtraction of two-digit numbers with and without regrouping using the GPDC strategy.
 Prerequisites
Prerequisites
Children can perform subtraction of two-digit numbers.
Introduction: Word Problems in Addition
The teacher may start with the revision of subtraction of two-digit numbers, followed by the introduction to word problems through a strategy called – Goal Plan Do Check (GPDC).
Resource required:
- Whiteboard and markers
- Word problem cards or worksheets
- Base-ten blocks (optional)
- Math journals or student notebooks
- Chart for GPDC steps
I Do
Teacher Models using the GPDC strategy to solve a Word problem
Word problem: Example
Sunita has 28 garlands. She gave 15 to her friend. How many are left now with Sunita?
Model Using GPDC:
- Goal: To find the number of garlands left with Sunita after giving 15 garlands to her friend.
- Plan: What do I need to do?
I need to subtract 15 from 28 to find the number of garlands that are left with Sunita. - Do: Solve the problem.
Explain step-by-step, showing if regrouping is required or not.
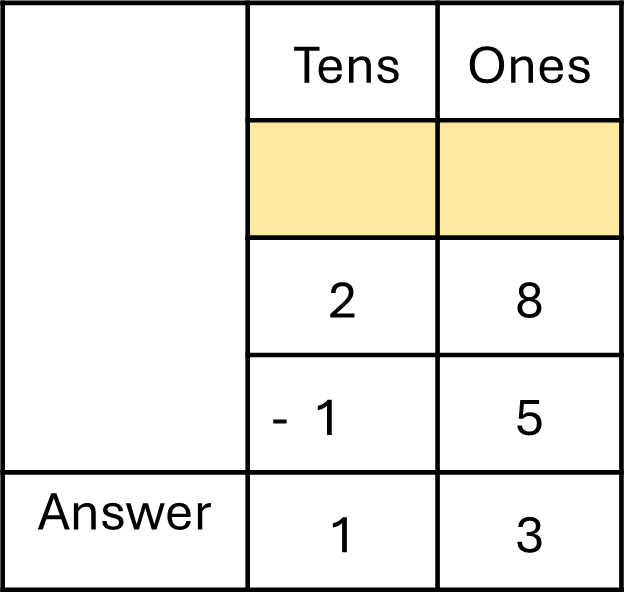
- Check: Does my answer make sense? Recheck by subtracting again.
Yes. I subtracted correctly, and the answer is less than the total number of garlands.
We Do
The teacher and children solve together using the GPDC strategy.
Word problem: Example
Sunil saw 46 cars in the parking lot. 29 cars left in the afternoon. How many cars are there now?
Guide children to solve step-by-step:
- Goal: To find the number of cars left in the parking lot.
- Plan: Subtract 29 from 46
- Do:
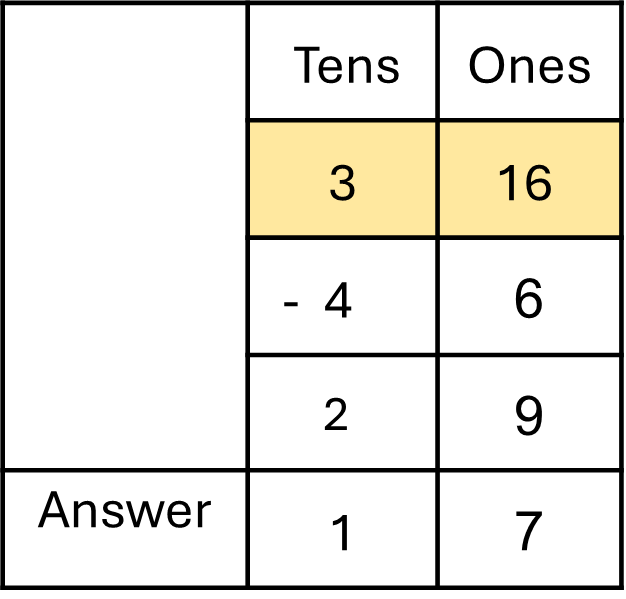
Is regrouping needed? Yes. One ten will regroup as ten ones.
- Check: Reread the problem and check the subtraction.
Ask prompting questions:
- What did we do first?
- Why did we regroup?
- Does the answer match the story?
We Do (Independent Practice):
Children solve word problems independently using the GPDC strategy.
Distribute 3 to 4 word problems (a mix of with and without regrouping).
Example:
- Rohan picked 54 apples for the fruit salad party. 25 apples were used. How many apples are left?
- There were 45 books on a shelf in the library, and 14 books were taken by the children. How many books are left on the shelf?
 Note to the teacher:
Note to the teacher:
- Use visuals for the word problems.
- Children will write out each step of the GPDC Strategy in their notebooks.
- Use base-ten blocks or number lines to solve the problem for visual learners.
Poster: GPDC Strategy – Coming soon
Video: Introduction to word problems in subtraction – Coming soon
ISL Video: Introduction to word problems in subtraction – Coming soon
Activity 1: Back from the Market
Objective:
Children will use the GPDC strategy to solve real-life subtraction problems involving shopping and calculating change.
Importance of the activity for children:
Helps in developing:
- Gross motor skills (Moving around, bending, stretching to pick things)
- Fine motor skills (Picking things, handling money)
- Cognitive skills (Calculation, critical thinking, problem solving)
- Social skills (Cooperation, playing together, discussing)
- Language skills (Articulating, communicating)
- Emotional skills (Builds confidence in numeracy, promotes a sense of achievement that boosts self-esteem, and encourages pride in learning new skills)
Resources required:
- Toy grocery items or empty packages
- Two-digit price tags
- Play money or paper currency
- Shopping baskets or bags
- GPDC recording sheets or notebooks
- Labels for each ‘shop’ section
Setting for the activity:
Set up a mock grocery market with items displayed and a checkout area in the classroom or any other spacious hall.
Type of activity: Tactile / Role Play
Preparation of activity:
- Label all grocery items with two-digit prices.
- Prepare play money sets (bills and coins).
- Set up tables or shelves for different departments.
- Print and distribute GPDC recording sheets.
- Arrange checkout stations with calculators if needed.
Role of the teacher: Demonstrator, observer and facilitator.
Procedure:
- Give each student a fixed amount of play money (e.g., Rs. 65).
- Children shop for 1 or 2 items and calculate the total cost.
- They use the GPDC strategy to find how much money they will get back.
- Goal: To calculate the remaining balance after making a purchase.
- Plan: Subtract item cost from starting amount.
- Do: Solve using subtraction (regrouping if needed).
- Check: Use play money or a calculator to verify the result.
- Record the steps on the GPDC worksheet.
Observations:
The teacher observes the children engaged in the activity to find:
- Are the children regrouping correctly when needed?
- Are the children able to identify the correct operation (subtraction)?
- Are the children able to use the money manipulatives meaningfully?
- Can the children explain their thinking?
Suggested Variations:
- Add a ‘tax’ component to the price to increase the difficulty level.
- Let children create their own word problems for peers.
- Include multi-step word problems (e.g., buy two items, find change)
Conclusion:
This activity reinforces real-world application of subtraction and fosters critical thinking through a familiar, practical context. Children also become more confident using the GPDC method independently.
Video: Back from the market – Coming soon
ISL Video: Back from the market – Coming soon
LTM: GPDC recording sheet – Coming soon
Activity 2: Subtraction Puzzle Walk
Objective:
Children will solve subtraction word problems involving two-digit numbers by physically moving to solve, search, and complete a puzzle using the GPDC strategy.
Importance of the activity for children:
Helps in developing:
- Gross motor skills (Moving around, bending, stretching to pick things)
- Fine motor skills (Picking things, handling money)
- Cognitive skills (Calculation, critical thinking, problem solving)
- Social skills (Cooperation, playing together, discussing)
- Language skills (Articulating, communicating)
- Emotional skills (Builds confidence in numeracy, promotes a sense of achievement that boosts self-esteem, and encourages pride in learning new skills)
Resources required:
- Laminated subtraction word problem cards
- Puzzle pieces with subtraction answers
- GPDC worksheets on clipboards
- Tape to post problems and answers
- Optional: timers, buzzers, or reward tokens
Setting for the activity:
- Open indoor space, hallway, or outdoor area
- Word problems and answer cards taped to different walls or objects
Type of activity:
Kinesthetic / Math Adventure
Preparation of activity:
- Write or print 5 to 10 subtraction word problems on large cards.
- Create answer puzzle pieces (e.g., form a math image or phrase).
- Scatter and tape cards around the activity area.
- Prepare the GPDC templates on clipboards.
Role of the teacher: Demonstrator, observer, and facilitator.
Procedure:
- Divide the class into small groups or pairs.
- Each group starts at a word problem station.
- They solve the subtraction problem using the GPDC strategy:
- Goal: To find a solution to the word problem.
- Plan: What are the numbers? What mathematical operation is appropriate?
- Do: Perform subtraction (with/without regrouping as required).
- Check: Reread the problem and verify the answer.
- After solving, the children find the matching answer puzzle piece kept somewhere in the display area.
- The children continue solving puzzles and collecting the answer card until the puzzle is complete.
Observations:
The teacher observes the children engaged in the activity to find:
- If the children can correctly identify when to regroup.
- If the children demonstrate understanding of GPDC steps independently?
- If the children are cooperating and communicating effectively?
Suggested Variations:
- Add time challenges for each round.
- Mix in distractor puzzle pieces (wrong answers).
- Let children create new problems to add to the walk.
- Use subtraction problems with real-life themes (e.g., party planning, school supplies).
Conclusion:
This activity turns problem-solving into an adventure. It helps the children stay active while applying GPDC in real subtraction situations. Movement, collaboration, and visual reinforcement deepen their understanding.
LTM: GPDC worksheet – Coming soon
LTM: Word problem cards – Coming soon
LTM: Puzzle with answer – Coming soon
Home Activity
Worksheet: Word problems – Coming soon
Worksheet: Word problems (Enlarged) – Coming soon
Cross-Curricular Connection:
- Language:
Reading comprehension: Children read and interpret word problems carefully.
Writing: Children write their own addition word problems or journal their steps using the GPDC strategy.
For example: Write a short story problem using characters from your favorite book.
Sequence and explain the steps of solving a problem using complete sentences. - EVS:
The teacher can talk about ‘deforestation’ and show pictures of an area before and after it occurred.
Children can then find out how many fewer trees are left.
Assessment
The teacher can provide a practice worksheet, which can be followed by an assessment worksheet, to assess the children’s understanding of the concept of subtraction.
Practice Worksheet – Coming soon
Practice Worksheet (Enlarged) – Coming soon
Assessment Worksheet – Coming soon
Assessment Worksheet (Enlarged) – Coming soon
Check list for teacher:
| Activity | Yes | No | Sometimes |
| Children can: | |||
| Subtract two-digit numbers | |||
| Children will solve word problems involving the subtraction of two-digit numbers with and without regrouping using the GPDC strategy | |||
| Children can create word problems involving subtraction | |||
| Focus on the activity | |||
| Complete the activities in the given time | |||
| Do the activities independently | |||
| Express verbally and through actions, expressions, or gestures | |||
| Enjoy teamwork, appreciate others, and are willing to learn from others |
Adaptations for addressing learner variability: Adaptations and strategies – Coming soon
Teacher Resource Document – Coming soon
| Source and Attribution of images: All images used in the above Assets and Aids are originally created. |
| This digital material has been developed by the Sri Sathya Sai Vidya Vahini Inclusive Education Project, a unit of Sri Sathya Sai Central Trust, Prasanthi Nilayam, as a collaborative offering in the service of our nation. |